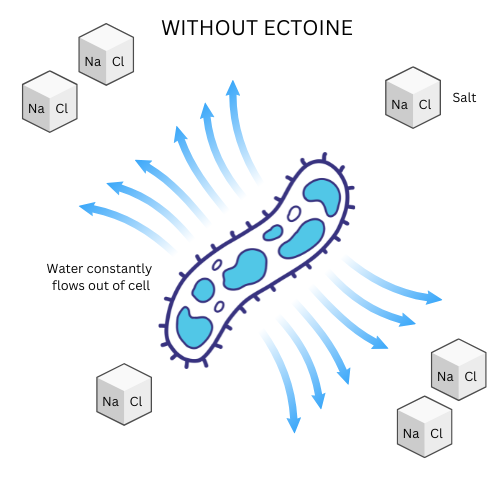
Ectoine is a naturally occurring compound that is produced by halophilic bacteria that survive high-salinity or high-salt environments. Ectoine acts as an osmolyte or osmoprotectant by regulating the movement of water out of the bacteria into the salty environment due to the natural osmosis process or high osmotic pressure.
In natural osmosis process, water will flow across a membrane or barrier from the lower salt concentration side to the higher salt concentration side. For a cell or bacteria, this is deadly as the cell or bacteria will just dry up and die. The bacteria produces and retains ectoine as a means to increase its osmotic pressure thus preventing the flow of water out of it.
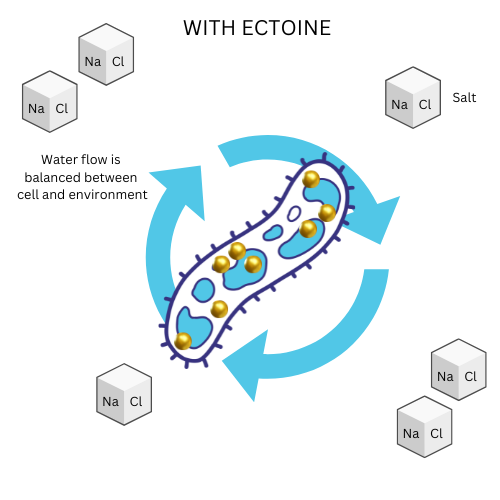
Ectoine binds to water molecules and prevents water loss while stabilizing proteins and membranes. It enables the bacteria to survive heat, freezing or dryness because their proteins and membranes are protected from drying out.
Ectoine thus makes it possible for these bacteria to survive in high-salt environments. These type of bacteria can be found in places such as the Great Salt Lake in Utah in America and the Red Sea and Dead Sea in the Middle East.
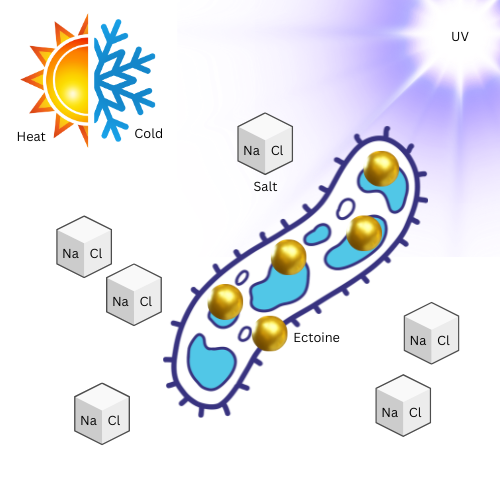
Ectoine also protects DNA against ionizing and ultraviolet radiation and also scavenges free radicals.
You may see products having ectoin (without “e”) instead of ectoine in its list of products. Ectoine is the name of the compound whereas Ectoin (without “e”) is its trade name. They both refer to the same compound.
Ectoine is produced industrially by placing the halophilic bacteria in a high-salt medium with appropriate nutrients to mimic its habitat and allow it to ferment the nutrients and biosynthesize ectoine. The bacteria is then “shocked” in a low-salt medium. The bacteria will rapidly release its ectoine into the medium in order to adapt to the low-salt environment. Ectoine is extracted from the medium by using a combination of extraction, separation and purification.
Some of ioula’s facial products contain ectoine precisely for its water retention, protein and membrane stabilization, anti-ultraviolet and anti-free radical properties. Ectoine strengthens your skin barrier by preventing dryness of your skin, strengthening its structure and membrane and offer you some sun protection. As an added benefit, strengthened skin is less likely to be irritated, thus you would be less inclined to scratch and cause further physical damage to your skin.
