Before we explain more about “what” ceramide is, let’s understand where you can find it on your skin first.
The outermost layer of your skin called the stratum corneum consists of many layers of your skin cells. The older skin cells are on the surface of your skin and they are more compressed than the lower layers. These cells are held together by a lipid matrix or what you can think of as a fat/oil matrix. The lipid matrix itself is composed of 50% ceramides, 25% cholesterol, 15% fatty acids and the remaining 10% is a mixture of other lipids in differing quantities. The lipid barrier forms a water-impermeable barrier and also prevents entry of microorganisms into your body. The combination of the lipid barrier and skin cells forming the stratum corneum is your skin barrier. A healthy skin barrier prevents TEWL (transepidermal water loss) which is water and moisture loss through your skin and also prevents skin infections.

There are many types of ceramide. Research shows that psoriasis may be caused by an increase in AS and NS ceramides and deficiencies in EOS, AP and NP ceramides causing a defect in the skin’s water impermeability barrier. The ceramide molecule base length and fatty acid chain length may cause a particular ceramide structure to be upregulated or downregulated leading to atopic dermatitis and also psoriasis.
Newborn babies are born with a waxy, cheese-like white substance coating their skin known as the vernix caseosa. Ceramide is a component of this coating. Our body constantly produces ceramide and its production is affected by your health, the environment and age. Drinking enough water, getting enough sleep and avoiding stress are important. Environmental factors such as hot showers, dry weather such as heated rooms and winter air can dry out your skin as well. Naturally, as you age, your body also produces less ceramide.
What is ceramide?
So what exactly is ceramide? It is a waxy lipid (fat) molecule that is found in high quantities in the sphingomyelins of our cell membranes. There are 12 types of ceramide contained in our skin. From our earlier explanation above, you understand now that it is an important component of our skin.
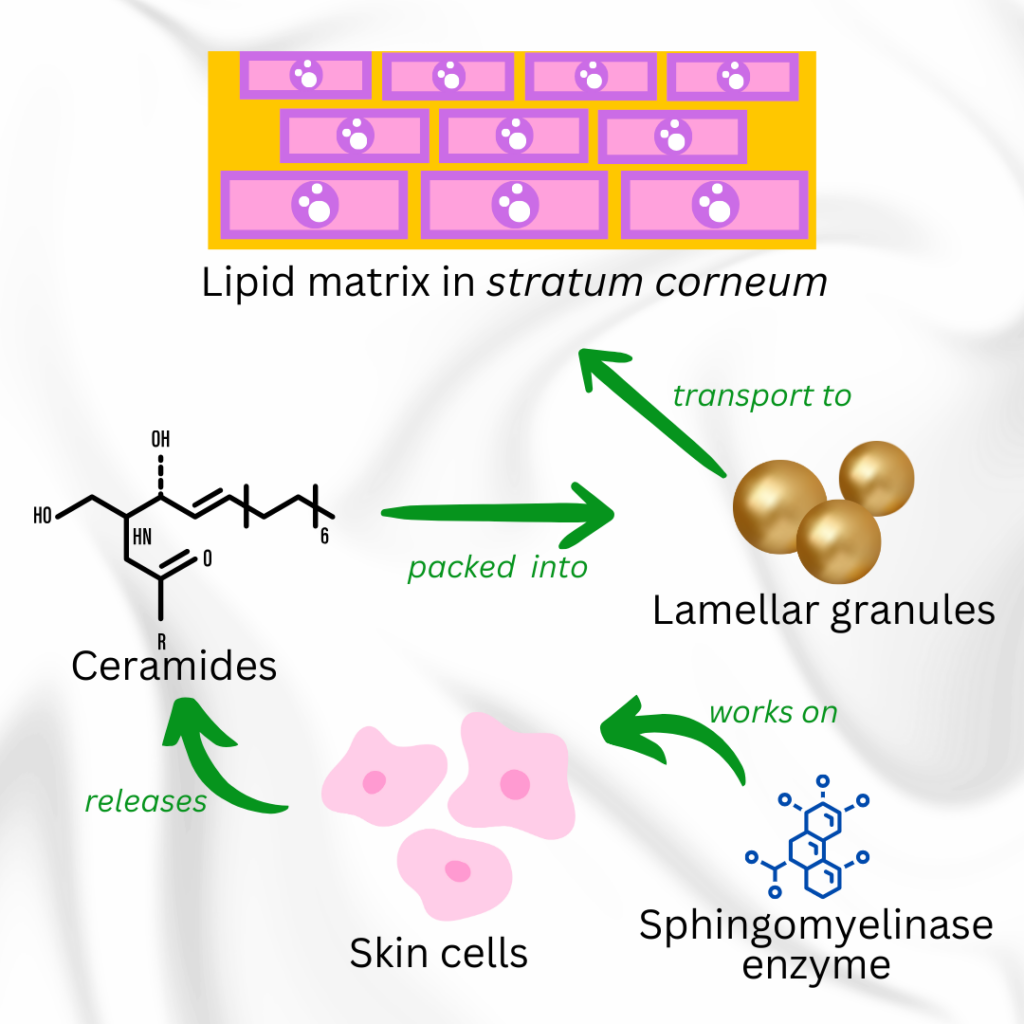
The process to produce ceramide is described below :
- Ceramide in your skin is produced by keratinocytes (skin cells).
- The enzyme sphingomyelinase breaks down sphingomyelins in the cell membranes to release the ceramide.
- The ceramide is then packed into lamellar granules that travel up through the layers of our skin to our stratum corneum.
- The ceramide then mingles with cholesterol, fatty acids and other lipids to form the lipid matrix that holds all the skin cells together to form the stratum corneum.
Ceramide for skincare
Ceramide for skincare can be produced from animal or plant sources. The ceramide we use in ioula is derived from plant sources that has been filtered after extraction to ensure purity. ioula has 5 of the 12 types of ceramide that are present in our skin. We include Ceramide AS, Ceramide AP, Ceramide EOP/EOS, Ceramide NS and Ceramide NP.
The ceramide in skincare products can help us replenish ceramide in our skin and also boost certain types of ceramide we may be lacking. We had read earlier that people with psoriasis have excess Ceramide AS and NS but have deficiencies in Ceramide EOS, AP and NP.
ioula also includes cholesterol as it is one of the components of our skin’s lipid matrix.
